Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture
Within computing architecture is a set of rules and methods that describe the functionality, organisation, and implementation of computer system. This applies to both the hardware and the software.
Computer architecture is the design of how components are connected and work together within a computer system. You must understand the implications of the current computer architecture models and the impact of relationships between the components and the system.
Computer Architecture Models
There are different approaches to computer architecture, the model that you will choose will depend on the factors and implications that need to consider.
We will be looking at the following architecture models:
- Stored Programmed Model
- Von Neumann Architecture
- Harvard Architecture
Store programmed model is the storage of instruction in a computer memory to enable it to perform a variety of tasks in a sequence or intermittently.
The CPU then processes data according to the sets of instructions CPU can handle billions of instructions per second and as long as the instructions are valid and referenced data within the program's boundaries, the control unit execute them if not, the computer stops the program from running.
info
This idea was first introduced in the late 1940s by Jhon Von Neumann who proposed that programs be electronically stored in binary format in the memory of the device some instructions could be modified by the computer as determined by intermediate computational results.
info
Bottleneck occurs when the capacity of an application or a computer system is limited by a single component. This problem occurred when using Von Neumann Architecture.
Problem 1 – Every data and programs share the same memory space. This is a problem because it is quite easy for a poorly write or faulty piece of code to write data into an area holding other instructions, so trashing that program.
Problem 2 – Every piece of data and instruction has to pass across the data bus in order to move from main memory into the CPU. This is a problem because the data bus is a lot slower than the rate at which the CPU can carry out instructions.
- The idea of the Harvard Architecture is to split the memory into two parts.
- One part for data and another part for programs
- Each part is accessed with a different bus. This means the CPU can be fetching both data and instruction at the same time.
- There is also less chance of program corruption.
Computer Architecture - How it Works
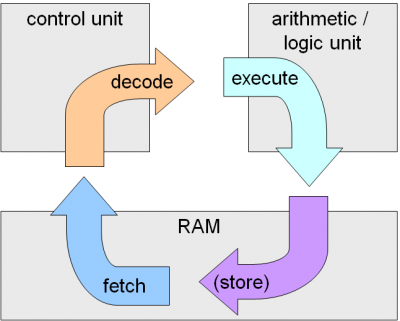
The purpose of the processor is to fetch and execute instructions.
The CPU consists of the following components:
- Arithmetic logic unit (ALU): performs calculations and logical decisions.
- Control unit (CU): sends signals to control how data moves around the CPU.
- Cache: provides fast access to frequently used instructions and data.
- Register:
- Program counter (PC)holds the address of the next instructions in memory.
- Memory address register (MAR): holds the address of where data is to be fetched or stored.
- Memory data register (MDR): holds the data fetched from, or to be written to the memory.
- Accumulator (AC): holds the results of calculations.
Buses
Buses are the means by which data is transmitted form one part of the computer to another, connecting all major internal components to the CPU and memory. A standard CPU system bus is comprised of a control bus data bus and address bus.
| Bus | Process |
|---|---|
| Address Bus | helps to transfer memory addresses while the data bus helps to send and receive data. That is, the address bus is used to specify a physical address in the memory while the data bus is used to transmit data among components in both directions. |
| Data Bus | carries the data between the processor and other components. |
| Control Bus | carries control signals from the processor to other components. The control bus also carries the clock's pulses. |